Unified Python Interactive Command Modules (ICM) and ICM-Players
A Framework For Development Of Expectations-Complete CommandsA Model For GUI-Line User Experience
Version 0.3
December 13, 2018
http://www.by-star.net/PLPC/180050
Summary
When writing Python software, your code is usually one of:
- Python Functions (part of a larger system) or Libraries
- Python Scripts – to be executed at command line
- Web Services – performers (servers) to be used by invokers (clients)
Unified Interactive Command Modules (ICM) is a framework that allows you to make your code be any or all of the above – with near zero extra effort.
ICM permits you to automatically map Python callables to command-line – similar to click. ICM also permits you to automatically map Python callables to Web Services operations – similar to Java’s DropWizard.
Since “Unified Commands” embed their full information about their arguments and outcomes within themselves, it is possible build to generic GUI’s for ICMs that can drived the formation of their command line.
Benefits Of This Commands Oriented Approach
Benefits Of Building On Top Of “Operations” and “Commands”
Augmenting Python at its most basic level with the concepts and abstractions of “Commands” and “Operations” has many benefits.
Scripting, Web Services And More Than Unit Testing
- Python code in the form of “Commands” becomes immediately invokable at command-line-interface. Python scripting is simplified and made consistent.
- Since “Commands” are derived from “Operations” and since they can be made “Remote Operations”, we can use Swagger (OpenApi) to build Web Services based on Commands.
- Since Commands are Python callables that are easily executable from outside of the code, they are easily testable.
Commands Are Abstract Expectations Complete
Abstract Expectations Of Commands
- Every Command “knows” with what options, parameters and arguments it may be called.
- Every Command “knows” the syntax of its results.
Command Expectations Are Emitable
- Every Command can emit its full parameter expectations.
- Every Command can emit its full results syntax information.
ICM-Players: User Interfaces That Fulfill Command Expectations
ICM-Players Are Generic Fancy UIs That Build Command-Lines Since each Command can fully tell us – “emit” – its full expectations, we can build different types of user interfaces that present these expectations to the user.
The user can then specify these inputs in stages to produce complex command-lines.
Precedence: Other Similar Approaches
There is ample precedence for each of the 3 aspects that the ICM model puts forward:
- Automated Mapping Of Command-Line To Python Callables
- Automated Building Of Web Services Based On Collection Of Callables
- Generic UIs that Invoke The Command-Line Or The Web Service
Automated Mapping Of Command-Line To Python Callables
Argparse/Optparse/Getopt. Built into Python. Complex. [Compago](https://github.com/jmohr/compago) Very nice, but unmaintained. Also, does not run on Python 3. [Docopt](http://docopt.org/) [Clint](https://github.com/kennethreitz/clint) [Click](http://click.pocoo.org/3/) https://pypi.python.org/pypi/snakeshell/0.4.0
Automated Mapping Of Command-Line To Python Callables
The concept and terminology of “Command” and “interactive” come from elisp (emacs lisp). But they have been modified and enhanced. In elisp:
The (interactive) special form declares that a function is a command, and that it may therefore be called interactively (via M-x). The argument arg-descriptor declares how to compute the arguments to the command when the command is called interactively.
A command may be called from Lisp programs like any other function, but then the caller supplies the arguments and arg-descriptor has no effect.
Therefore, in elisp the concepts of “Command” and “interactive” are directly linked. We consider that a mistake.
With ICMs “Command” and “interactive” are independent concepts.
Automated Building Of Web Services Based On Collection Of Callables
Java's dropwizard
Generic UIs that Invoke The Command-Line Or The Web Service
Swagger-UI
Specialized ICMs – Libraries, Packages, APPs And Frameworks
ICM is a foundational building block.
Concept of ICM is language independent, a practical subset of the capabilities of Python-ICM has been implemented as BASH-ICM.
MARMEE and GOSSONoT are examples of ICM Based Packages and ICM higher level frameworks.
Related Documents
Remote Operations Interactive Command Modules (RO-ICM)
Best Current (2018) Practices For Web Services Development
http://www.by-star.net/PLPC/180056 — [2]
A Generalized Swagger (OpenAPI) Centered Web Services Invocations And Testing Framework
http://www.by-star.net/PLPC/180057 — [1]
Bash Interactive Command Modules (Bash-ICM)
http://www.by-star.net/PLPC/180058 — []
Obtaining The Software
You can obtain complete source-code for ICM from:
PyPi Pip Install
pip install unisos.icm pip install unisos.icmExamples
Github Repos
https://github.com/unisos-pip/icm
https://github.com/unisos-pip/icmExamples
Part Of ByStar DE and BISOS
ICM is Part Of A Much Bigger Picture.
ICM Is Part Of:
The Libre-Halaal ByStar Digital Ecosystem
And Part Of:
BISOS: ByStar Internet Services OS
ICM is being used and developed in that context.
About This Presentation/ScreenCast
You can obtain this document at its access page:
where it is available in multiple forms and multiple formats:
-
Article/Book Form: Best suited for cover-to-cover reading (pdf).
- Pdf Format: Best suited for printing and cover-to-cover reading.
- HTML/Web Format: Best suited for Web reading and cross referencing.
- Presentation Form: Best suited for quick scan – with live URLs –(pdf).
- Screencast: A slide oriented voice-over narrated presentation (Reveal.js Based)
- PDF Slides: Best suited for printing of the slides (Beamer Generated)
- HTML Slides And Notes: Slide and notes in html format (Beamer+HaVeA Generated)
- PDF Slides and Notes: Best suited for printing of presentation notes (Beamer Generated)
In addition to pdf presentation format, this information is also available in article format.
The pdf Article file is best suited for printing and cover to cover reading.
Additionally, this information is available as voice-over presentation format, where audio files are played sequential with the slide.
All of these formats are available in one place on the Access Page of this document at the
mentioned URL
It is best to refer to this screencast and document based on its Access Page number.
Let’s now continue with the real content of this presentation.
Document Outline:
- The Unified Commands Model, Concepts And Terminology
- The Model Of ICM-Players And ICM-Apps
- ICM Specializations
- Direct And Remote Operations – Direct ICMs, Remote ICM Invokers, Remote ICM Performers
- Direct ICMs Command-Line Structure And Model
- Overview Of The unisos.icm Package
- Current Status And Next Steps
Unified Commands
Command (Unified Command)
A “Command” is a user invokable execution entry point.
A Unified Command can be invoked from:
- The Command Line Interface – (Foreign, Local, Interactive)
- Through A Web Services (Remote Operations) Invoker – (Foreign, Remote)
- Python Code – (Native, Local)
Terminology Of Native vs Foreign, Local vs Remote, Interactive vs Non-Interactive
Native Vs Foreign
Invocation of Commands can be “Native” (an ordinary call) or “Foreign” (a framework call).
Local Vs Remote Invocation of Commands can be “Local” (same process and machine) or “Remote” (different process or different machine).
Interactive Vs Non-Interactive For the purposes of the invokation an abstract Human-User may exist (interactive) or an abstract Human-User does no exist (non-interactive).
Terminimogy Of Callables, Operations And Commands
Operations Are Special Forms Of Callables
Operations are Callables whose arguments and results are “foreignly” specified.
Commands Are Special Special Forms Of Operations
Commands are Operations which are expection complete
Commands Are Special Forms Of Operations
Commands As Operations
Each Command has:
- A cmndName (an opName)
- Operations Arguments In The Form Of:
- Cmnd-Options
- Cmnd-Parameters
- Cmnd-Arguments
- Operation Results In The Form Of:
- stdExit, stdOut, stdErr
- opOutcome
Commands Are Patterned After Operations
Commands Are aware of Command-Line
Each Command expects to be invoked from the command-line and is aware of Command-Line to python-callable mappings.
Commands Have Embedded In Themselves Full Arguments And Results Information
class Cmnd
Each Cmnd, through its methods can output its:
- Cmnd-Name
- Cmnd-Description
- Expected Parameters (and description of each expected Parameter)
- Expected Arguments (and description of expected Arguments)
- Expected outcome
Commands Have Embedded In Themselves Full Arguments And Results Information
class Cmnd
Is aware of how it has been invoked (Command-Line, Web Services, Python) and can validate its expectations.
Commands Have Embedded In Themselves Full Arguments And Results Information
When Invoked As Interactive
Commands get their parameters from command-line.
Commands write to their stdout, stderr
When Invoked As Non-Interactive
Commands get their parameters to have been passed to them in full.
Comands may avoid writing to their stdout, stderr
Interactive Command Modules (ICMs) As Collections Of Related Commands
Collection Of Related Commands
When related Commands are grouped in a python module with a common __main__ entry, they for an “Interactive Commands Module (ICM)”.
Related And Common Parameters
Collection Of Related Commands
Parameters specification for different commands may be shared in an ICM.
An Overview Of ICM Framework, Modules And Players
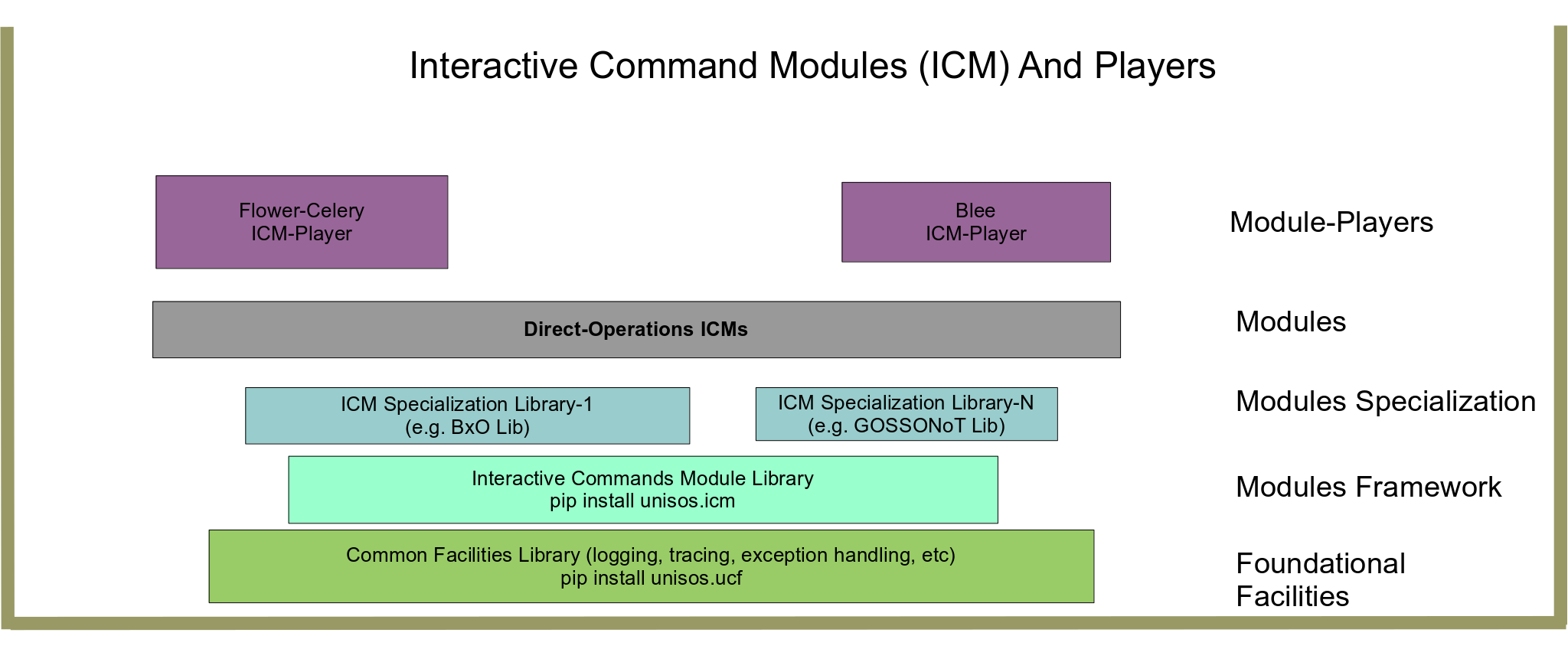
Interactive Command Modules (ICMs) As Collections Of Related Commands
About ICM Players Based on the ICM’s self-contained info, ICM modules can be used at cmnd-line or through auto-generated User-Interfaces.
The Blee-ICM-Player (With Emacs and elisp)
Blee-ICM-Player
An emacs based ICM-Player has been implemented.
Abstraction Of ICM-Apps
ICM-Apps:
When a group of ICMs wish to have a UI which is more specialized than ICM-Players, custom UIs for their commands can be built.
That packaging of the custom UIs and the ICMs is called and ICM-App.
About BASH-ICMs
Concept of ICM is language independent.
In Python, Commands are implemented as a Class that encapsulates the expectations within the “Class Cmnd”.
In Bash, Commands are special forms of Bash functions.
A practical subset of the capabilities of Python-ICM has been implemented as Bash-ICM.
See BASH-ICMs for more details.
ICM Groupings
- ICM
- ICM.Packaged
- ICM.Packaged.basicPkg – Marme
- ICM.Packaged.toiimPkg
- ICM.Packaged.empnaPkg
- ICM.Grouped
- ICM.Grouped.Bisos
- ICM.Scattered(bxt)
- ICM.Scattered.mailingsProc
- ICM.Unitary – A Single ICM
- ICM.Standalone – A Single ICM With Library Included – Distributable
About ICM Libraries – Collections Of Reusable ICMs
ICM “Commands” can be included in ICM-Libraries which can then be combined.
Development Workflow
Python Invocation Inputs: Complex Arguments
Python Invocation Outputs: Complex Return Values
Command-Line Invocation Inputs: Options And Args
Command-Line Invocation Outputs: stdout, stderr
Remote-Operation Invocation Inputs: parameters Remote-Operation Outputs: Results, Errors
You just write your python code, the CLI and Remote Operations are fully auto generated.
Benefits And Powers Of The ICM Unified Model
Most of your development life-cycle is in a local and single process environment.
At will you map to command line.
At will you can split the functionality to remote-operations (Web Services).
You can switch between the three models by maintaining a single code base.
ICM Performer Responders
ICM-Commands are directly invoked.
In a single process model where parameters and arguments and results are through the command line and file system.
An Overview Of Direct-Operations ICMs and ICM-Players

Convertable To Web Services Performer
Auto Generation Of Web Services Performer
Since ICMs are expectation complete, their expectations can be converted to a swagger-file.
The swagger-code-generator will then use the swagger-file to generate web-services code.
Commands within the ICM then become “controllers” that the generated code uses.
All of this can be fully automated such that an ICM becomes a web-service performer without any coding.
Web Services ICM With Swagger Code Generators

Common Direct ICMs Command Syntax And Model – Python And Bash Specific Features
Model And Terminology of Direct-ICM Command-Line is based on:
- CmndsModule – icmCmndsModule
- Cmnds – cmndName
- Cmnd Options – optionName1 ... optionNameN
- Cmnd Params – parmName1 ... paramNameN
- Cmnd Args – arg1 ... argN
Which leads to the common ICMs command-line invocation syntax of
icmCmndsModule --optionNameN --parmNameN=paramValueN -i cmndName arg1 argN
Python and Bash ICMs, each have their own specific additional features.
Python DO-ICM Features
- –examples – Frequently Invoked Menu Examples
- –help – Usage – getopt Summary
- Logging
- Tracing and Debugging
- –load – Run time additional code loading
Frequently Invoked Menu Example
Running the ICM with no options, params, cmnds or args or using the --examples option produces frequently invoked menu examples. The examples menu is often tailored to desired usage patterns. This is the best way of getting started.
Usage –help
Running the ICM with --help provides the usual getopt usage information.
Logging
With -v 30 -- default -- ICM results go to stdout. With -v 20, ICMs also report Swagger specified inputs and output with -v 15, ICMs also report http traffic as seen by requests with -v 1, ICMs also report digestion of the swagger file
Tracing And Debugging
You can enable run time tracing of key callables (those decorated with @icm.subjectToTracking) by including: -v 1 --callTrackings monitor+ --callTrackings invoke+
Plugins – Loading Of Additional Python Code
Additional code can be added to an ICM at run time with the --load additionalCode.py
Python Method Invocations Of Commands
Commands can also be invoked from python. The cmnd() method of the icm.Cmnd() class needs to be called with interactive=False. Below is a demonstrational simple example.
icm.cmndList_mainsMethods().cmnd(
interactive=False,
importedCmnds=g_importedCmnds,
mainFileName=__file__,
)
See unisos.icmExamples pip package for more details.
ICM-Performers
Remote Operations Interactive Command Modules (RO-ICM)
Best Current (2018) Practices For Web Services Development
http://www.by-star.net/PLPC/180056 — [2]
ICM-Invokers
A Generalized Swagger (OpenAPI) Centered Web Services Invocations And Testing Framework
http://www.by-star.net/PLPC/180057 — [1]
Wrappers And Streams
pip install unisos.ucf
Wrappers And Streams
Add to warpers ICM-Instantiate
Common ICM Parameter – Out Stream Consumer/Usage Context –oUsage=icmPlayerBlee
Wrappers And Streams
pip install unisos.ucf
Wrappers And Streams
Python’s Abstract Syntax Tree (AST) is searched to locate all class Cmnd declarations, through which the mapping to the cmnd method is facilitated.
ICM-Invokers
In the context of ByStar and BISOS, both Python-ICMs and Bash-ICMs have been in use for more than a decade.
With the exception of full automation of web services conversion all features and capabilities mentioned in this document have been implemented.
Next Steps
ICM is now ready for general use.
If you use it, please send us your feedback.